Why infrared is probably the best heating principle for halls and what the GEG has to do with it.
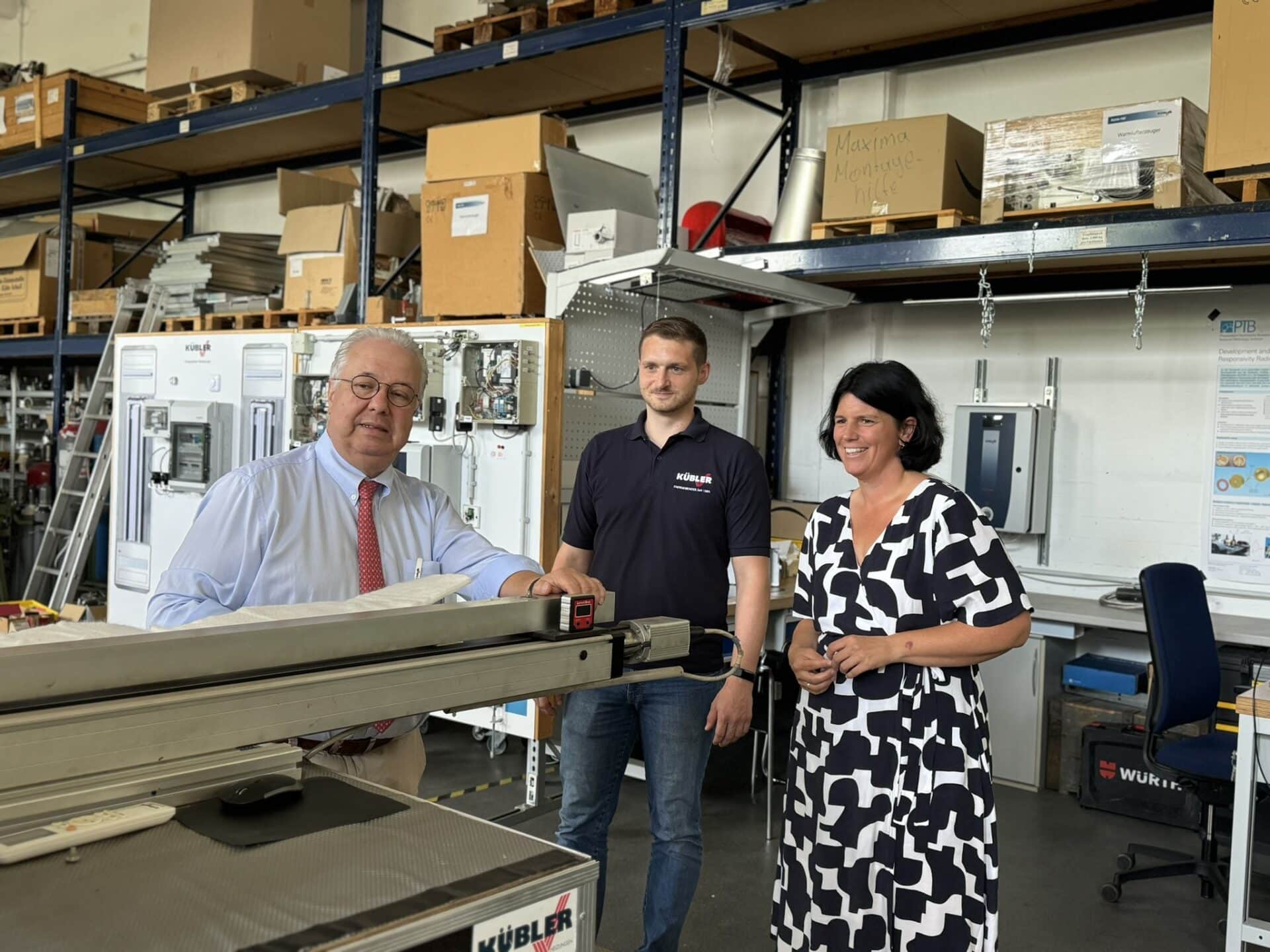

"I came to understand the technology," says Carina Konrad as Thomas Kübler begins his presentation and apologizes for the perhaps somewhat dry subject matter. There was a good reason why the deputy state chairwoman of the FDP in Rhineland-Palatinate and deputy chairwoman of the FDP parliamentary group in the Bundestag made her way to Ludwigshafen:
"KÜBLER shows how it is possible to combine climate protection and economic efficiency through innovative technologies such as infrared heating. We must do everything we can to spread these practicable solutions in public discourse and anchor them in widespread use," says Carina Konrad. The top politician therefore wanted to find out first-hand how established industrial companies can make the energy transition economically and technically viable.
What is needed here are solutions that are so economical that the switch to renewable energies gives the industry a competitive advantage. "This is only possible with technologies that have a high level of usability and maximum energy efficiency with an investment that is economically viable," says Thomas Kübler.
Carina Konrad emphasizes the important contribution that medium-sized companies like KÜBLER in particular make: "Germany's greatest contribution to climate protection is to use its own engineering power to develop technologies that are in demand on the market due to their economic advantages in application. KÜBLER shows what is possible in 35 years of company history. We need more of this," said Konrad. During her visit to Ludwigshafen, Konrad made it clear that a political rethink must also take place here. Thanks to the Free Democrats' participation in the government, the Building Energy Act in the residential sector has been adapted to make it technology-neutral. Politics must create the conditions for the potential of all technologies to be exploited. This approach should also be ensured in the area of industrial and commercial buildings, as focusing on a single technology (i.e. the heat pump) is not very functional there. The deputy FDP state and parliamentary group leader in the Bundestag describes the preservation of productive jobs in Germany as one of the most important tasks of politics, although she is aware that the development of energy resources via renewable energies and the hydrogen strategy in Germany require sufficient time.
At the moment, whenever people talk or write about heating and the energy transition, there is only one focus: Residential buildings and, at most, offices or similar multi-storey buildings. But there is also another type of building: Industrial and commercial buildings. Nobody talks about hall buildings, says Thomas Kübler. And the BMWK also seems to have largely lost sight of this type of building in the Building Energy Act. Yet huge industrial and commercial halls - only 2 percent of all heated buildings in Germany - consume enormous amounts of energy. To be more precise: around 15 percent of the total annual energy consumption for space heating in Germany!
This is a figure that is highly relevant for the energy transition and could already be reduced by 50 to 70 percent today with the help of long-established and proven decentralized infrared technology. An enormous contribution on the way to climate neutrality, which also pays off economically for companies and can compensate for the current competitive disadvantages in Germany, such as high energy prices.
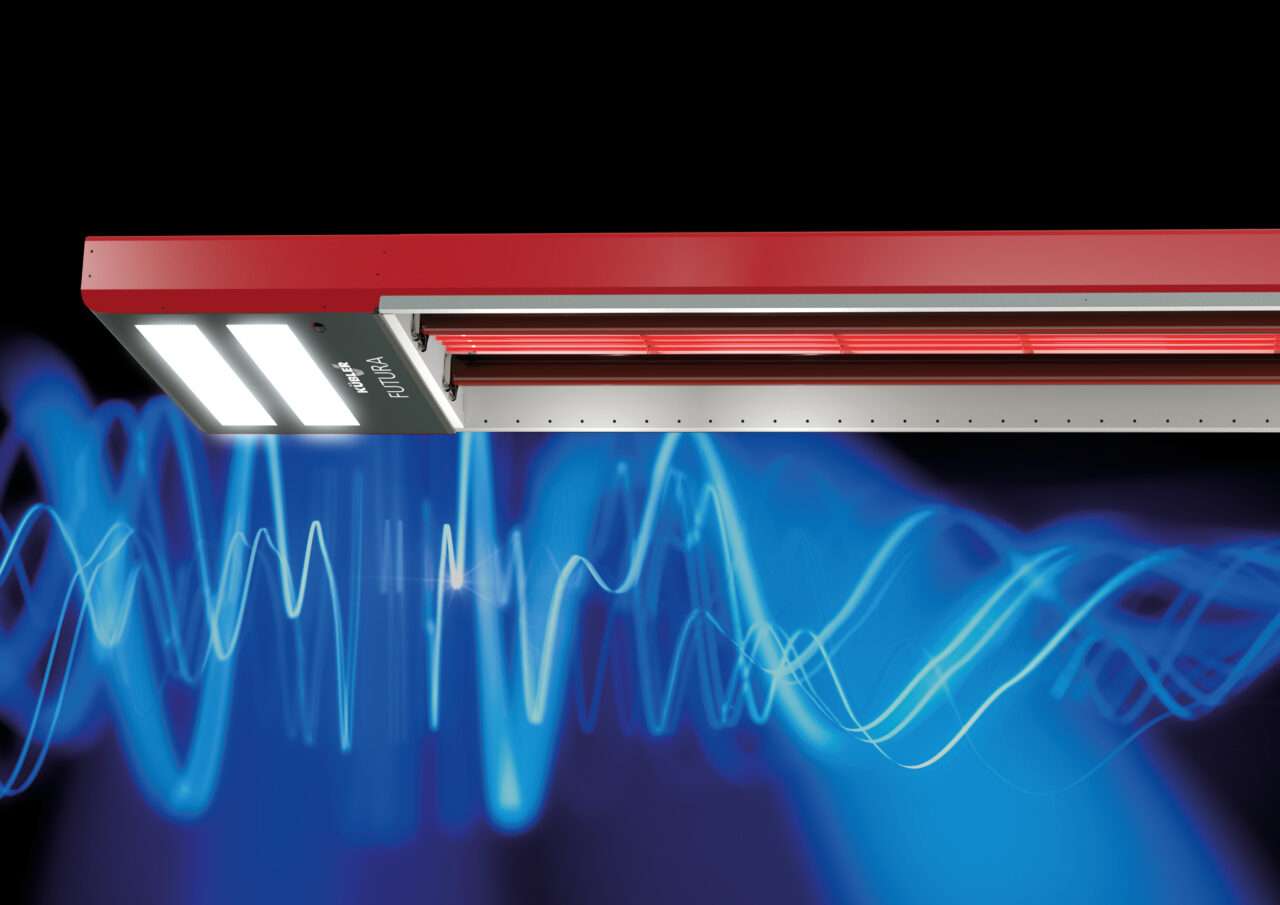
The latest generation of infrared heaters can be heated with electricity, PV power or even hydrogen in an energy-flexible manner and could already reduce the heat supply in industry and commerce to zero CO2 decarbonize. With absolute security of supply - another important point for companies. For Carina Konrad, it is crucial that a clear political perspective for innovations such as infrared heating in new buildings is created as quickly as possible.
At the end of the conversation between Carina Konrad and Thomas Kübler and the insights into the technology, it became clear that the natural heating principle of infrared is actually quite simple to explain. Just as the sun heats the part of the earth's surface that it hits with its rays from a distance of 149,597,870 km, infrared heaters from hall heights of 8, 10, 20 meters and more heat the area of use in the lower hall area. Quite simply according to the laws of physics, loss-free and therefore highly efficient.
Carina Konrad and Thomas Kübler agree that more needs to be said about halls and their very specific heating requirements, if only because of their height and volume. They also agree that there is an urgent need for more exchange between political decision-makers, science and the commercial enterprises that, like KÜBLER, have the practical technical expertise and are developing innovations in Germany for the energy transition.

Company visit to hall heating specialist KÜBLER in Ludwigshafen: Carina Konrad, deputy state chairwoman of the FDP in Rhineland-Palatinate and deputy chairwoman of the FDP parliamentary group in the Bundestag, and Thomas Kübler, managing partner, in front of a model of the technology leader's new infrared heating development. (Source: KÜBLER GmbH Energiesparende Hallenheizungen)

KÜBLER's R&D laboratory not only produces award-winning hall heating innovations for decarbonization, it is also where the process was developed that is now used to measure infrared efficiency worldwide: Top politician Carina Konrad FDP, Thomas Kübler and Dr. Steffen Manser in conversation. (Source: KÜBLER GmbH Energiesparende Hallenheizungen)
-
As of today, it's clear: the world first from KÜBLER has won its third award! Following the SUCCESS 2022 Technology Award and the Rhineland-Palatinate 2023 Innovation Award, the innovative FUTURA multi-energy IR heating system for the climate-friendly and economical heating of hall buildings has now been recognized in the "Winner" category of the German Innovation Award 2023.
-
Minister President Malu Dreyer: Rhineland-Palatinate is an attractive location with a home and future for many strong, imaginative companies
-
The German government wants 65% renewable energy from 2024. "It can have it," says Thomas Kübler, founder and Managing Director of KÜBLER GmbH from Ludwigshafen. The hall heating specialist is presenting its latest developments and world firsts at the ISH. These are three systems that enable companies to save money and play their part in the energy transition.
-
Gas is decentralized, flexible, can be stored efficiently and is inexpensive. The energy source is a guarantee for the success of the energy transition. Ten associations from the gas industry have joined forces and formulated an appeal for the climate protection plan, explaining why gas as an energy source can already achieve significant CO2 savings cost-effectively today.