No energy transition without an economic policy transition

From 6th place to 24th place in just ten years, our once leading industrial nation according to the IMD Competiveness Ranking 2024[1] slipped. 45 percent of industrial companies with high electricity costs are planning or implementing plans to reduce their production or relocate it abroad. Rising trend[2]. Increasing bureaucratic costs and the extremely high energy prices in our country are causing existential problems for many companies, in addition to the shortage of skilled workers. And the new Building Energy Act (GEG) adds another misguided measure.
Ever since the BMWK's concept paper "65% renewable energies for the installation of new heating systems from 2024" announced the contents of the new GEG in July 2022, Thomas Kübler has been warning of the technical errors in the hasty and ideologically driven amendment to the law. He knows all about the Heating Act.
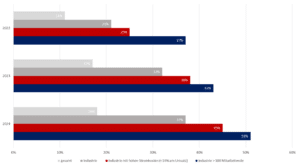
Source: "Energy transition barometer 2024", DIHK, evaluation-energiewende-barometer-2024-data.pdf
"The good news is that there are technically excellent and economical solutions for industrial and commercial buildings to successfully implement the heating transition under affordable conditions," says the experienced specialist in energy-saving hall heating technologies. For non-energy-intensive companies - the lion's share of businesses in Germany - the heating transition is the most important lever for decarbonization. As a rule, over two thirds of energy is used for heating. The fatal thing, according to Thomas Kübler, is that politicians made a whole series of mistakes when drafting the GEG, but against their better judgment are not prepared to rectify them in the current legislative period. Particularly in the area of new construction, the law indirectly stipulates the technology instead of CO2-The BMWK's aim is to set goals and leave the path to the goal to the companies, which already have more expertise and solutions than the political establishment in the BMWK. The restriction to the heat pump preferred by the BMWK for all building types without recognizing the special heating features of halls is bound to go wrong, says Kübler. And would be about as dysfunctional as going on vacation with a concrete mixer. Or like transporting concrete in the trunk of the family car. Both are possible, but not sensible.
In the GEG, politicians continue to equate residential and office buildings, hotels and kindergartens with production or logistics halls. Instead of using the knowledge of specialists to develop correct and functional solutions, they prefer to pursue a landlord-style energy policy. No wonder the energy transition is stumbling.
Berlin is even turning a blind eye to much more suitable technologies for heating hall buildings. Even the latest developments in heating technology, with enormous potential savings of 50 to 70 percent in energy consumption and the corresponding GHG emissions, and the ability to already meet the climate targets of 2045 with renewable energies, are receiving little to no political attention. What remains is the innovation clause in Section 103 of the GEG. Thankfully, this bureaucratic route at least opens up the opportunity to use sensible solutions for tall hall buildings, says Kübler. However, this requires cooperation with the manufacturer, as the relevant information has not yet been legally introduced into the relevant calculation programs used by TGA engineers. As is so often the case in Germany, everything is made more complicated than necessary. Yet it is precisely these heating technologies that will make an important contribution to reducing energy costs and CO2-emissions for companies and thus counteract the relocation of important jobs abroad.
"What does this mean for your company, are you also thinking of relocating abroad?" we ask Thomas Kübler. "We have no plans to emigrate. And we're not sticking to the roads either," says the entrepreneur. Instead, he relies on education and knowledge transfer for political decision-makers. "It's time that basic knowledge about gravity became more important than ideological half-knowledge." He is convinced that if the economy acted as superficially as Berlin is currently treating Germany as a business location, there would be a hail of warnings and dismissals.
[1] https://www.imd.org/centers/wcc/world-competitiveness-center/rankings/world-competitiveness-ranking/rankings/wcr-rankings/#_tab_Rank
[2] Electricity prices: How the energy transition is driving industry out of Germany (handelsblatt.com)
You can also read the article in the Handelsblatt: No energy turnaround without an economic policy turnaround! - Handelsblatt Live
-
The topic of Industry 4.0 is no longer a dream of the future. The digitalization of industrial processes is being talked about everywhere - and a new era has also dawned in the heating supply sector. Find out in this article what intelligent networking looks like for heating building complexes and what opportunities it opens up for you!
-
Room volume, employee requirements, climate protection targets, heating costs and, and, and: When choosing the right heating system for your halls, you need to consider a whole range of factors. Read this article to find out what these are in detail and how you can master these challenges with a modern system.
-
Infrared hall heating in your production: How to create the right indoor climate for your productionIndoor buildings are a world of their own. Especially in winter. The high rooms pose a real challenge for anyone who wants to ensure the most pleasant working climate possible. But there are solutions - infrared hall heating, for example.
-
Outdated hall heating systems lead to horrendous heating costs and pollute the environment. Despite this, many operators shy away from investing in modernization. One possible solution: rented hall heating systems - heat-as-a-service!