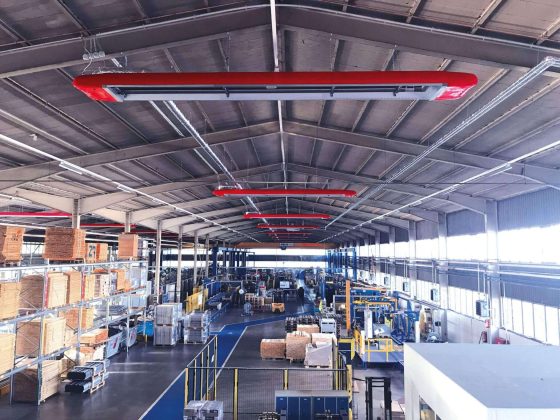
Heating halls with 65 percent renewable energy - but the right way

What is the concept paper "65% renewable energies for the installation of new heating systems from 2024" about? And what does this have to do with the refurbishment of existing heating systems in hall buildings? In this concept paper, the German government plans to make the use of 65% renewable energies mandatory from 2024. In addition, the maximum operating time of heating systems powered purely by fossil fuels is to be shortened from 2026. This means that heating systems will have to be replaced when they are 20 years old.
What does it mean for you and other operators of hall buildings if this concept paper is implemented? From our point of view as experts in sustainable hall heating, there are three options:
Option 1: Replace your existing heating system in 2023 with one of KÜBLER's proven energy-saving systems, use condensing boiler technology where it makes sense, but save yourself the additional costs of a hybrid multi-energy system first.
Result: In our experience, the modernization measure will reduce your heating energy consumption by 50 to 70 percent. This leads to a considerable reduction in CO2-footprint and your consumption costs, so that the investment usually pays for itself in two to three years. In the future, you can easily adapt the new heating system as soon as hydrogen is available in sufficient and affordable quantities.
Option 2: You opt for the high-efficiency system from KÜBLER, thus taking advantage of the hydrogen option and the possibility of upgrading the heating system at any time and easily with the retrofit kit for electricity or PV use. As a result, you can expect the same benefits as shown in option 1.
Option 3: You invest directly in CO2-freedom with a multi-energy system from KÜBLER that allows you to use different renewable energy sources such as electricity or hydrogen as well as gas or biogas variably - in a mix or alternatively.
The bottom line is that this option gives you the freedom to rely on your own PV power immediately, for example, and thus achieve a degree of energy self-sufficiency. Active energy management via the control system allows you to reduce heating costs and CO2-emissions are scalable when using different energy sources - what progress!
To summarize: it has never been so easy to implement the transformation to the carbon-free era in your hall buildings. And under economic conditions. This is because the investment is comparatively low - it is around 3 times lower than for heat pumps, for example. If you also use the lucrative HeizWerk rental model, you benefit from ultra-modern and highly functional hall heating technology even off-balance - i.e. without your own investment and depreciation costs. At the same time, your consumption costs will be reduced so significantly (usually by 50 - 70 percent) that you will have a cost advantage even when renting.
By the way: The innovative multi-energy system was awarded the special prize "Innovative technologies for climate protection" at the SUCCESS technology competition at the end of 2022 and has been nominated for the German Innovation Award in 2023.
-
The German government's targets are ambitious: by 2045, Germany is to be climate-neutral and dispense with fossil fuels in the production of heat. A target that is putting pressure on the industry. Numerous innovations are pushing for the switch to renewable energies - such as the German Fuel Emissions Trading Act (BEHG), which has led to an increase in CO2-price for fossil fuels.
-
The energy crisis is currently leaving no one indifferent. Everyone is desperately looking for ways to get consumption and costs under control to some extent. The German government's price brake will not take effect until March 2023, and even then, the prices for 30 percent above the basic quota for industry and 20 percent for small and medium-sized enterprises will still be subject to the wild market conditions next year. So what to do?
-
Only around half of German companies are aware of their waste heat potential - this is what dena writes in its publication on waste heat utilization as part of the Energy Efficiency Initiative. This means that an estimated 226 TWh of usable heat goes unused every year. That is 36 % of the energy used by the entire manufacturing industry. Clearly, this costs companies an enormous amount of money, but at the same time the unused waste heat has a negative impact on the environment. Around 60 million tons of the greenhouse gas CO2 are unnecessarily evaporated into the atmosphere every year. In view of rising energy costs and climate protection targets, companies simply can no longer afford to do this.
-
The search for suitable optimization potential in energy-related processes in industrial and commercial companies is not always easy for energy management. Especially as measures in efficiency technologies and renewable energies cost money and the budget is often lacking. Many - ecologically and economically important - measures then fall by the wayside. But does that have to be the case?